Influenza A/B test kits are crucial tools for rapidly diagnosing flu infections. These kits enable healthcare providers to quickly identify the presence of influenza viruses in patients, allowing for timely treatment and management. Healthcare professionals need to understand how to accurately interpret the results of these tests to ensure proper patient care. This blog post will provide an in-depth guide on best practices for interpreting influenza A/B test kit results.
Understanding Influenza, A/B Testing Kits
Influenza A/B testing kits serve as vital diagnostic instruments for identifying the presence of influenza viruses in individuals showing flu symptoms. These kits are designed in various formats, including lateral flow assays and molecular testing methodologies such as PCR, to accommodate the diverse needs of healthcare settings. Lateral flow assays are celebrated for delivering rapid results, usually within minutes, facilitating swift decision-making in clinical environments.
On the other hand, molecular tests generally require a longer processing time and are distinguished by their higher sensitivity and specificity, making them invaluable in scenarios where accuracy is paramount. The utility of these kits extends beyond mere detection; they play a pivotal role in streamlining patient management and treatment strategies by quickly distinguishing between influenza A and B viruses, each of which may necessitate a different approach to care.
The Importance of Rapid Flu Diagnosis
The timely identification of influenza infections through rapid flu diagnosis is instrumental in controlling the spread of the virus and ensuring effective patient management. The advantages of swift diagnosis are manifold, impacting individual patient outcomes and broader public health efforts.
Early Intervention and Treatment
A rapid diagnosis facilitates the commencement of antiviral treatments, which are most effective when started within the first 48 hours of symptom onset. This can significantly reduce the severity and duration of the illness.
Prevention of Disease Spread
Identifying influenza cases promptly enables healthcare providers to implement necessary isolation protocols and advise on preventive measures, thereby curbing the virus’s transmission within communities.
Resource Allocation
In healthcare settings, especially during flu seasons or outbreaks, quickly differentiating influenza from other respiratory infections allows for more efficient use of resources, such as isolation wards and antiviral medications.
Reduction in Healthcare Burden
By preventing flu-related complications through early treatment, rapid diagnosis can lead to a decrease in hospital admissions and a reduction in the overall strain on healthcare systems.
Informing Public Health Responses
Accurate and swift identification of influenza cases contributes to real-time surveillance data, aiding public health authorities in effectively formulating responsive strategies to manage and control flu outbreaks.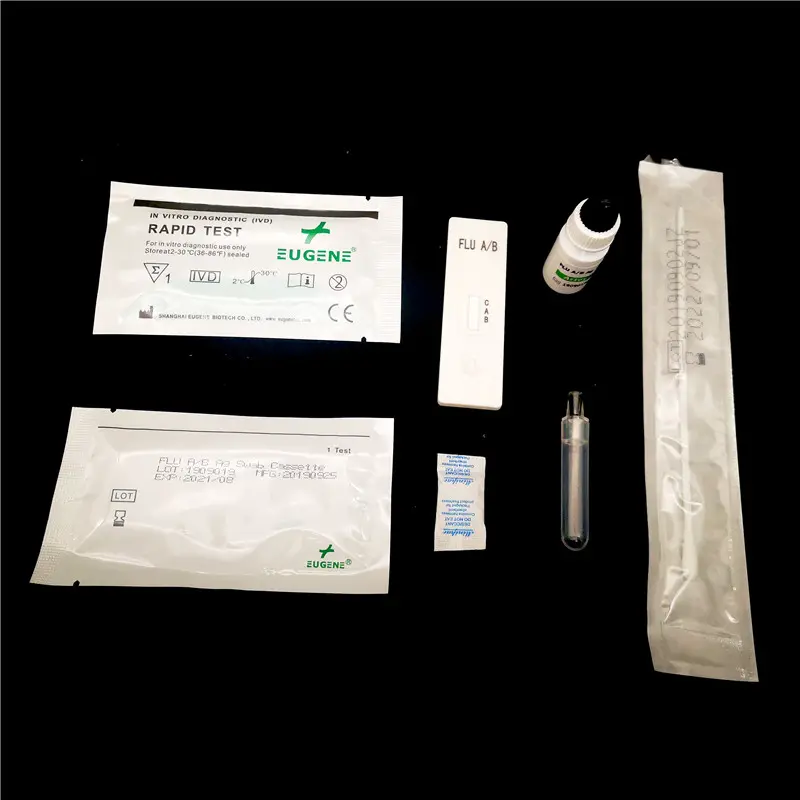
Components of the Influenza A/B Testing Kits
Components of the Influenza A/B testing kits comprise a meticulously designed ensemble, crucial for accurately detecting the influenza viruses. Each kit typically houses a test strip impregnated with specific antibodies with a high affinity for influenza virus antigens. When a sample collected from a patient is introduced to this strip via a buffer solution, these antibodies interact with any present influenza antigens, facilitating their detection.
The inclusion of sample collection swabs within the kit aids in the acquisition of respiratory specimens from patients, either through nasal or throat swabbing. These swabs are then immersed into a buffer solution provided within the kit. This solution is pivotal in liberating the virus particles from the sample, ensuring they come into contact with the test strip for analysis. The synergistic function of these components is fundamental in delivering reliable results from the influenza A/B testing process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting the Test
Conducting an influenza, A/B test requires precision and adherence to a specific procedure to ensure the accuracy of the results. This guide outlines the essential steps healthcare professionals should follow when using flu, A/B testing kits:
Preparation
Gather all necessary test kit components, including the test strip or device, buffer solution, and sample collection swab. Ensure the testing area is clean and free from potential contaminants.
Sample Collection
Using the provided swab, carefully collect a respiratory specimen from the patient. Depending on the kit’s instructions, this may involve swabbing the interior of the nose or the back of the throat.
Sample Processing
Immerse the collected sample swab into the buffer solution. This step is critical for releasing the virus particles from the specimen.
Applying the Sample
Transfer the processed sample onto the test device, usually by placing a specified amount of the solution onto the test strip or into a designated well on the device.
Reading the Results
After the recommended waiting period, which can vary by kit, interpret the results according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. This typically involves assessing the appearance of lines or symbols on the test strip or device.
By carefully following these steps, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose influenza A or B virus infections, facilitating timely and appropriate patient care.
Reading and Interpreting Test Results
In the context of influenza, A/B testing, the interpretation of results is categorised into three distinct outcomes: positive, negative, or invalid. A positive outcome signifies the detection of influenza virus antigens in the specimen, indicating an active infection. Conversely, a negative outcome implies the absence of these virus antigens, suggesting the patient does not have the flu.
However, there are instances where results may be deemed invalid. Such scenarios typically arise from procedural errors, such as incorrect sample collection or the mishandling of the test kit components. In these cases, the test fails to provide a conclusive outcome, necessitating a retest to acquire accurate data. Healthcare professionals must adhere to the specific guidelines set forth by the test kit manufacturer when interpreting these results to minimise the likelihood of error and ensure the validity of the diagnosis.
Familiar Sources of Error and How to Avoid Them
Errors in administering and interpreting influenza A/B testing kits can compromise the accuracy of results. Common pitfalls include inadequate specimen collection, leading to insufficient viral material for analysis. Moreover, incorrect storage conditions of reagents can alter their efficacy, whilst contamination of the test strip may introduce false results.
To mitigate these issues, it is paramount that healthcare providers adhere to rigorous training on specimen collection techniques, strictly follow the storage instructions provided by the manufacturer, and handle test kit components with utmost care to prevent contamination. Vigilance in these areas is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the testing process and ensuring reliable outcomes.
The Sensitivity and Specificity of Flu A/B Testing Kits
The performance of influenza A/B testing kits is measured through two critical parameters: sensitivity and specificity. Sensitivity encapsulates the kit’s capacity to accurately detect individuals infected with the influenza virus, thereby minimising false negatives. Conversely, specificity reflects the kit’s aptitude in identifying individuals who are not infected, effectively reducing false positives. These metrics are pivotal as they directly influence the reliability of the test results.
Higher sensitivity ensures that most infected individuals are correctly identified, which is crucial for initiating timely treatment and preventing further spread. Meanwhile, elevated specificity aids in avoiding unnecessary treatments or further testing for those not afflicted by the virus. It is imperative for healthcare professionals to carefully consider these factors, as variations in sensitivity and specificity among different kits can significantly impact clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
When to Retest: Guidelines for Reconfirmation
Determining the necessity for retesting individuals for influenza A/B is guided by several criteria that healthcare professionals must consider. This includes instances where the initial test result is inconclusive or does not align with the patient’s clinical symptoms. In situations where there is a significant discrepancy between the clinical assessment and the test outcomes, retesting may be advisable to ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Additionally, the emergence of symptoms consistent with influenza following a negative test result may warrant re-evaluating the patient’s condition. Healthcare providers are encouraged to adhere to established protocols for reconfirmation testing, which may involve using alternative testing methods or kits with higher sensitivity and specificity.
The decision to retest should be carefully weighed, considering the potential implications for patient care and the overall management of influenza within the healthcare setting.
Integrating Test Results into Patient Management
Integrating the results from influenza A/B testing into patient management strategies is a critical step for healthcare providers. Upon obtaining a positive outcome, immediate measures are initiated, including prescribing antiviral medication of stringent implementation and meticulously monitoring the patient; a negative result might suggest exploring alternative diagnoses or conducting further tests to pinpoint the underlying cause of the symptoms. This nuanced approach ensures that each patient receives a tailored management plan, optimising recovery trajectories and minimising the risk of contagion within the community.
Healthcare professionals are tasked with judicious application of these test results, crafting individualised care protocols that address each patient’s specific needs and health status.
Influenza Testing in Special Populations
Influenza testing in special populations requires a nuanced approach, considering these groups’ unique susceptibilities and potential for severe outcomes. Young children and elderly individuals often exhibit atypical flu symptoms, which may necessitate a higher index of suspicion and the potential for more frequent testing.
Pregnant women, due to their altered immune state and the risk to the fetus, also demand careful consideration when interpreting test results and deciding on subsequent management strategies.
Additionally, immunocompromised patients might not only present with muted responses to infection but also suffer from prolonged viral shedding, thereby complicating the diagnostic process. Tailoring testing protocols to accommodate these variances, alongside a keen understanding of the limitations and capabilities of influenza A/B testing kits, is crucial in ensuring accurate diagnoses within these vulnerable populations.
Comparing Different Brands of Flu A/B Test Kits
When navigating the market of Flu A/B Test Kits, healthcare professionals are presented with an array of options, each brand possessing its unique set of characteristics in terms of sensitivity, specificity, user-friendliness, and cost-efficiency.
The diversity among brands necessitates a careful evaluation to select a kit that aligns with the specific requirements of a healthcare setting. Factors such as the expected turnaround time for results, the prevalence of influenza types in the community, and the availability of resources for test administration should be considered.
Additionally, it is critical to opt for kits that have undergone rigorous validation processes, as confirmed by relevant health authorities, to ensure the reliability of diagnostic outcomes. Making an informed choice among different brands contributes significantly to the precision of flu diagnostics, ultimately influencing patient treatment paths and the efficacy of infection control measures within healthcare environments.
Innovations in Flu Testing Technology
Recent advancements in flu testing technology have heralded the introduction of cutting-edge influenza A/B testing kits. These innovations encompass rapid molecular tests that offer enhanced accuracy and reduced processing times, point-of-care devices that enable immediate decision-making in various healthcare settings, and multiplex assays capable of simultaneously detecting multiple respiratory pathogens.
Such developments are pivotal in refining diagnostic precision and expanding the capabilities of healthcare providers in managing influenza. Adopting these novel technologies supports a more nuanced understanding of respiratory infections, facilitating a targeted and efficient approach to patient care.
Conclusion
In summarising the discourse on influenza A/B test kits, it emerges that the precision in diagnosis these kits offer is indispensable in the clinical management of influenza. Their role extends beyond identification, impacting treatment pathways, infection control measures, and public health policies. Healthcare professionals are endowed with a responsibility to ensure meticulous adherence to testing protocols, thereby safeguarding the accuracy of results. This commitment to best practices in interpreting influenza A/B test kit results underpins the overarching aim of enhancing patient outcomes and mitigating the spread of influenza within communities.
FAQs
What differentiates influenza A from influenza B in testing?
Influenza A and B viruses are distinguished by their unique genetic and antigenic properties in testing scenarios. Test kits are designed with specific antibodies to detect these differences, allowing healthcare providers to identify the type of virus in the patient’s sample.
How long does receiving results from an influenza A/B test kit take?
The duration for obtaining results can vary depending on the type of test kit used. Lateral flow assays typically provide results within minutes, offering rapid diagnosis, while molecular tests, known for their higher sensitivity, may take longer to process.
Can a Flu A/B Test Kits be used at home?
Some Flu A/B Test Kits are intended for healthcare professionals only due to the need for precise sample collection and interpretation of results. However, there are also kits designed for home use, with detailed instructions to guide individuals through the testing process.
What should be done if a test result is inconclusive?
If a test result is deemed inconclusive, it is recommended that it be retested using a new test kit, preferably with a fresh sample. Inconclusive results can occur due to procedural errors or issues with the test kit.
Are influenza A/B testing kits effective in detecting current strains of the flu virus?
Influenza A/B testing kits are regularly updated to detect prevalent strains of the flu virus. However, the effectiveness can vary with emerging strains. Healthcare professionals often rely on guidance from health authorities and manufacturers regarding the current efficacy of test kits against circulating strains.
| Related Business Listings |
| Contact Directory |
| Local Business Profiles |
| Other Good Articles to Read |
| Cme Blog Spot |
| Garcias Blogs |
| Yyc Blogs |
| Guiade Blogs |
| Blogs-Hunt |
| Impact-Blog |
| Smarty Blogs |
| Ed Blog |
| Mo Blogs |
| Blogs Em |
| Blog St |